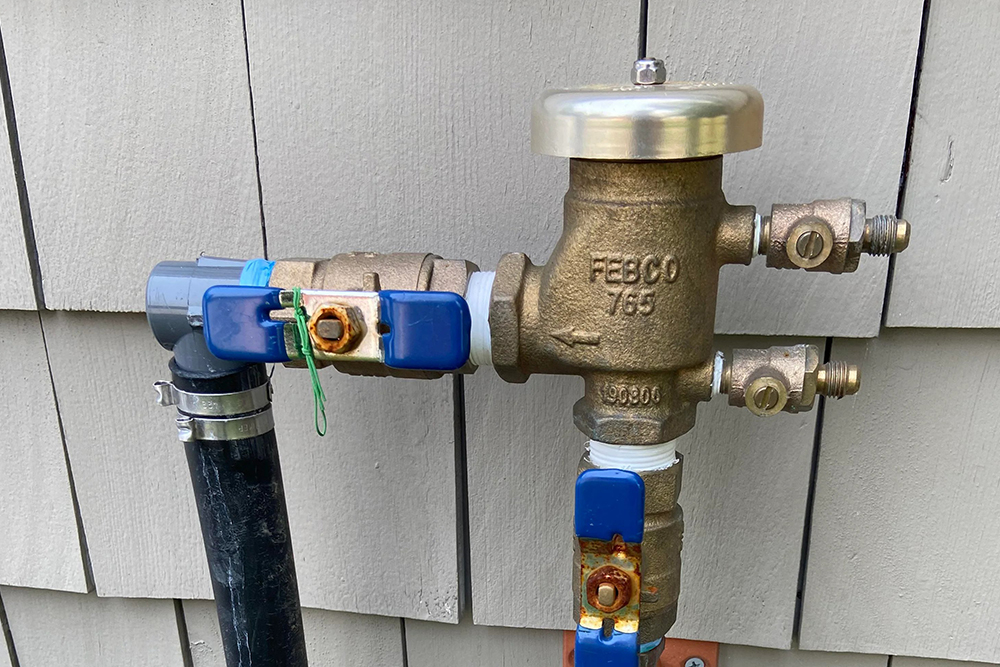
We assess our irrigation designs to incorporate backflow prevention. Backflow prevention is essential for protecting the potable water supply from contamination. Backflow occurs when the flow of non-potable water or substances is reversed and flows back into the main water supply, potentially contaminating it. To prevent backflow in irrigation systems, the following measures are typically implemented:
-
Backflow Prevention Devices: Backflow prevention devices are installed at key points in the irrigation system to prevent the reversal of water flow. These devices allow water to flow in one direction but prevent it from flowing back into the main water supply. The specific type of backflow prevention device required depends on the level of hazard and the local regulations. Common types of backflow prevention devices used in irrigation systems include:
a. Atmospheric Vacuum Breakers (AVB): AVBs are simple devices that prevent backflow by allowing air to enter the system when the pressure drops. They are typically installed at the highest point in the irrigation system and are suitable for low-hazard applications.
b. Pressure Vacuum Breakers (PVB): PVBs use a spring-loaded check valve to prevent backflow. They are installed at a point above ground level and are effective for medium-hazard applications.
c. Reduced Pressure Zone (RPZ) Assemblies: RPZ assemblies provide the highest level of backflow prevention and are used for high-hazard applications. They have two check valves and a relief valve to create a zone of lower pressure between the valves, effectively preventing backflow.
-
Local Codes and Regulations: Backflow prevention requirements may vary depending on local codes and regulations. It is important to consult with local authorities or a certified irrigation professional to ensure compliance with the specific backflow prevention regulations in your area. They can provide guidance on the appropriate backflow prevention devices and their installation requirements.
-
Education and Training: Users of the irrigation system should be educated about the importance of backflow prevention and the potential risks associated with backflow. Training programs and guidelines can help users understand the significance of backflow prevention and how to identify and report any issues or concerns related to backflow.